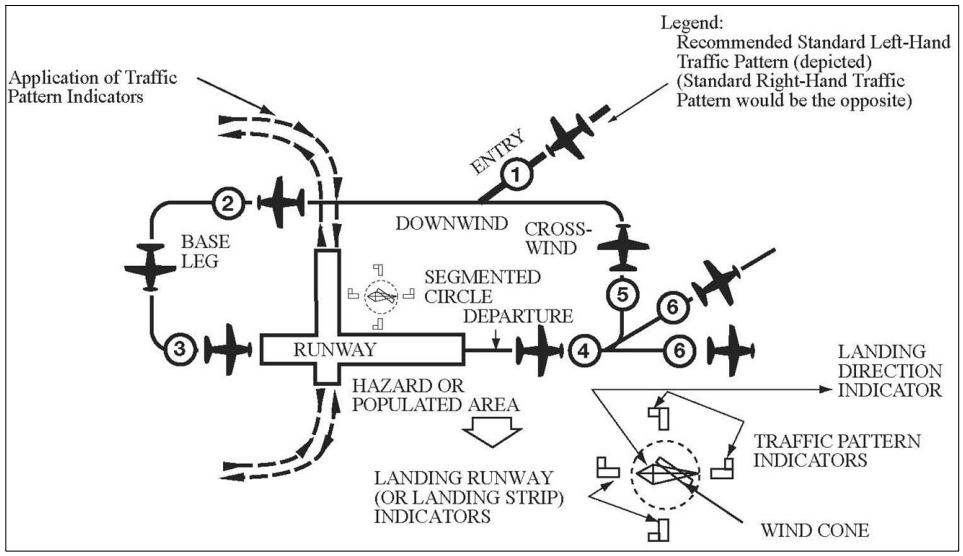
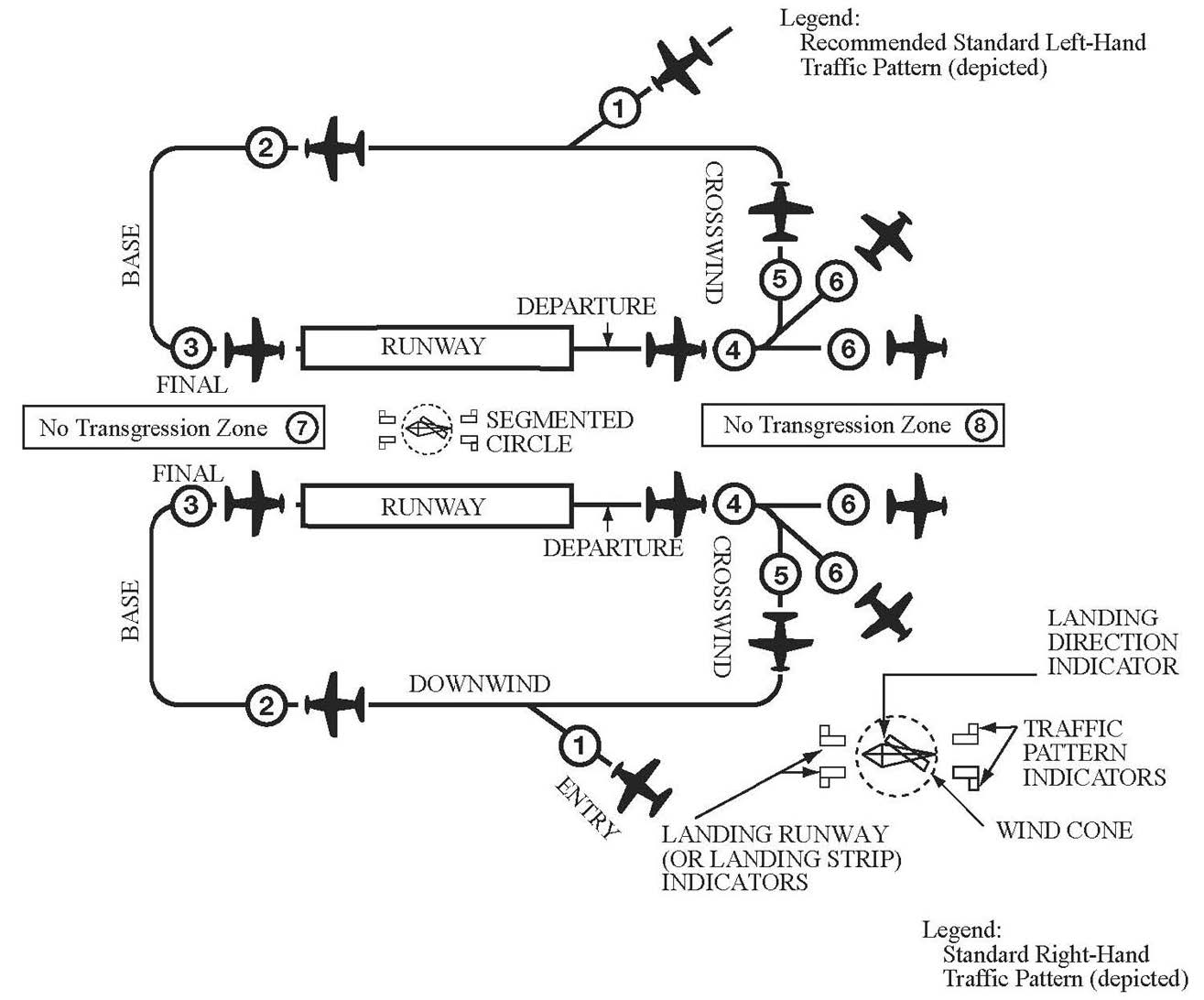
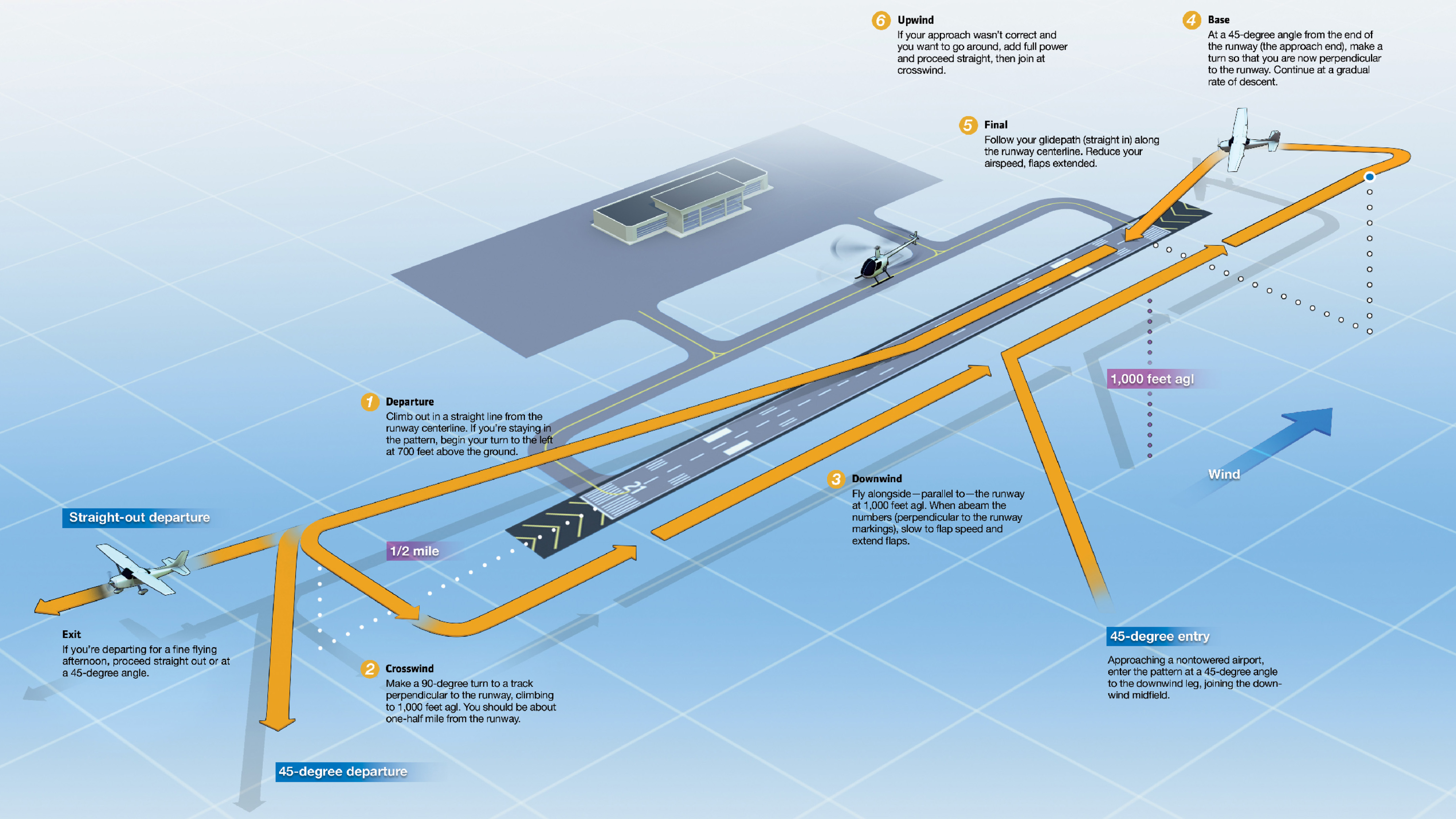
Aviation Traffic Pattern
Aviation Traffic Pattern - Web the traffic patterns provide specific routes for takeoffs, departures, arrivals, and landings. If there’s one thing that winds me up when in the traffic pattern, it’s following that cessna 150 flying an extended downwind before turning a 4 mile final, flying at 60 knots the whole way. Find further pattern information in the chart supplement, including traffic pattern altitude. The technique that’s worked best for me. The direction and placement of the pattern, the altitude at which it is to be flown, and the procedures for entering and exiting the pattern may depend on local conditions. Web traffic pattern procedures develop the ability to stay safely and efficiently arrive at an uncontrolled airport, or after arrival, utilize the traffic pattern. For a typical trainer such as a cessna 172, a “standard” traffic pattern is flown to the left and at 1,000 feet above ground level (agl). We aren’t flying airliners, so why fly an airliner traffic pattern? Indeed, the demand for air transport is. Web traffic pattern operations—single runway. We aren’t flying airliners, so why fly an airliner traffic pattern? At an airport, the pattern (or circuit) is a standard path for coordinating air traffic. Web tune in atis. Web the aircraft were flying in the pattern of the fun fly zone (ffz), which is located in the ultralight area. Far from the airport, tune the automated terminal information system (atis) frequency to learn your destination airport’s current weather and runway (s) in use. This air traffic operation becomes more complex and challenging as demands continue to increase. Web an airfield traffic pattern is a standard path followed by aircraft when taking off or landing while maintaining visual contact with the airfield. Web the faa has released updated guidance on how we pilots are expected to fly traffic patterns, and the updates are fairly extensive and for the most part really smart, too. These altitudes should be maintained unless another traffic pattern altitude is published in the chart supplement or unless otherwise required by the applicable distance from cloud criteria (14 cfr section 91.155). Web the airport traffic pattern is a means of safely directing aircraft in and out of an aerodrome. Web so, what is “the pattern”? Web the map appears to start around utc 00:00 on friday — or 8 p.m. Web traffic patterns provide procedures for takeoffs, departures, arrivals, and landings. This is the best and safest entry, because it enables you to see other pilots in the pattern and enables those in the pattern to see you. But. Know where to look for details on the pattern. Find further pattern information in the chart supplement, including traffic pattern altitude. (1,000′ agl is recommended pattern altitude unless otherwise established.) [figure 3] Business insider verified the map using flightradar24's playback feature. Web when i was a student, i learned the golden rule of standard traffic pattern entries: Web when i was a student, i learned the golden rule of standard traffic pattern entries: Eastern time on thursday — and shows air traffic for delta air lines, united airlines, and american airlines flights slowing down late into the night. Standardized traffic pattern for all types of ffz operations with exception of the. Web it is important to fly. Web traffic pattern operations—single runway. It’s the path you will fly when leaving and returning to the airport, specifically the runway. Web traffic patterns provide procedures for takeoffs, departures, arrivals, and landings. If you can hear milwaukee approach, i need. Web tune in atis. For a typical trainer such as a cessna 172, a “standard” traffic pattern is flown to the left and at 1,000 feet above ground level (agl). Web the traffic patterns provide specific routes for takeoffs, departures, arrivals, and landings. Most patterns are flown in a rectangle. Web traffic pattern operations—single runway. Indeed, the demand for air transport is. This is the best and safest entry, because it enables you to see other pilots in the pattern and enables those in the pattern to see you. Web the recommended entry position to an airport traffic pattern is to enter 45° at the midpoint of the downwind leg at traffic pattern altitude. Web in this video we look at the. Web the faa has released updated guidance on how we pilots are expected to fly traffic patterns, and the updates are fairly extensive and for the most part really smart, too. But as the sun rises and time reaches utc 12:00. After air force one landed, a group of local officials. Web the traffic patterns provide specific routes for takeoffs,. (1,000′ agl is recommended pattern altitude unless otherwise established.) [figure 3] Web the traffic patterns provide specific routes for takeoffs, departures, arrivals, and landings. The traffic pattern is comprised of several components which standardized flow of aircraft, at a. Web tune in atis. Standardized traffic pattern for all types of ffz operations with exception of the. Far from the airport, tune the automated terminal information system (atis) frequency to learn your destination airport’s current weather and runway (s) in use. While the airport traffic pattern is standardized, every traffic pattern is established based on conditions specific to each airport,. Pilots in the training phase often study the traffic pattern. Web traffic pattern operations—single runway. Web tune. Web knowing the traffic pattern, as well as how to correct for local adjustments to it, helps all of the pilots using it remain safe and organized, even if the airport is not outfitted with an air traffic control tower, or the tower is not staffed. Meanwhile, flights that were in the air already were allowed to continue. These altitudes. (1,000′ agl is recommended pattern altitude unless otherwise established.) [figure 3] While the airport traffic pattern is standardized, every traffic pattern is established based on conditions specific to each airport,. Web knowing the traffic pattern, as well as how to correct for local adjustments to it, helps all of the pilots using it remain safe and organized, even if the airport is not outfitted with an air traffic control tower, or the tower is not staffed. Web traffic pattern procedures develop the ability to stay safely and efficiently arrive at an uncontrolled airport, or after arrival, utilize the traffic pattern. Web the airport traffic pattern is a means of safely directing aircraft in and out of an aerodrome. Enter pattern in level flight, abeam the midpoint of the runway, at pattern altitude. Far from the airport, tune the automated terminal information system (atis) frequency to learn your destination airport’s current weather and runway (s) in use. These altitudes should be maintained unless another traffic pattern altitude is published in the chart supplement or unless otherwise required by the applicable distance from cloud criteria (14 cfr section 91.155). Web it is important to fly standard traffic pattern procedures to ensure the safe and orderly flow of aircraft to and from an airport. For a typical trainer such as a cessna 172, a “standard” traffic pattern is flown to the left and at 1,000 feet above ground level (agl). The exact nature of each airport traffic pattern is dependent on the runway in use, wind conditions (which determine the runway in use), obstructions, and other factors. Web traffic pattern operations—single runway. This air traffic operation becomes more complex and challenging as demands continue to increase. Indeed, the demand for air transport is. If there’s one thing that winds me up when in the traffic pattern, it’s following that cessna 150 flying an extended downwind before turning a 4 mile final, flying at 60 knots the whole way. Most patterns are flown in a rectangle.Procedures and Airport Operations Traffic Patterns Learn to Fly Blog
How to fly a standard airport traffic pattern Flight Training Central
Procedures and Airport Operations Traffic Patterns Learn to Fly Blog
Airport Traffic Patterns How Airplanes Avoid MidAir Collisions
Everything You Should Know About the Airport Traffic Pattern
Important Guide to Entering the Traffic Pattern Safely! Lets Fly VFR
How to Fly a General Aviation Traffic Pattern
Traffic Pattern Operations
Airport Operations
Technique The traffic pattern AOPA
Web Traffic Pattern Info.
Note The Atis Information Identification Letter—For Example, Hotel—Because It Changes With Each Update.
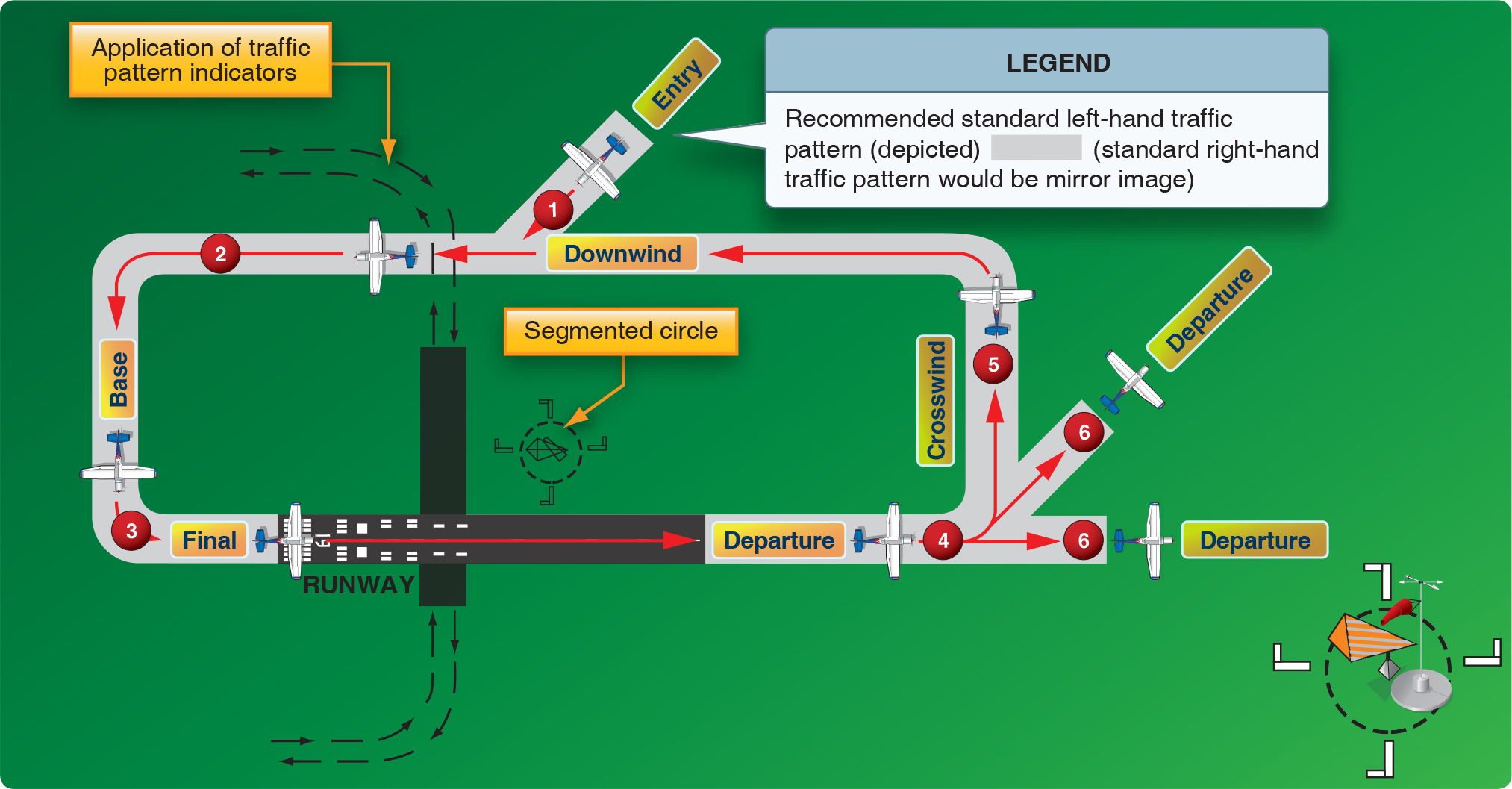
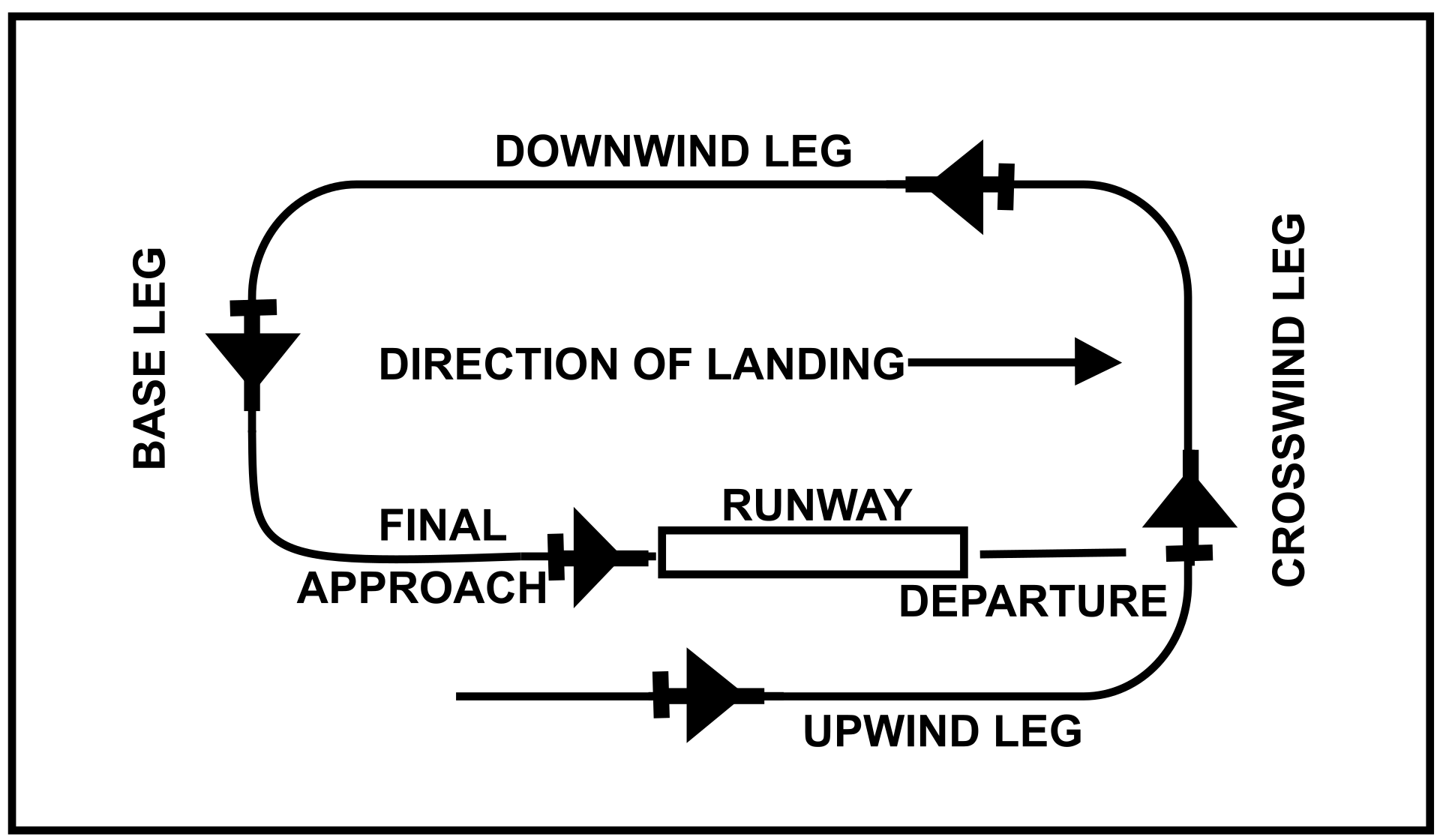
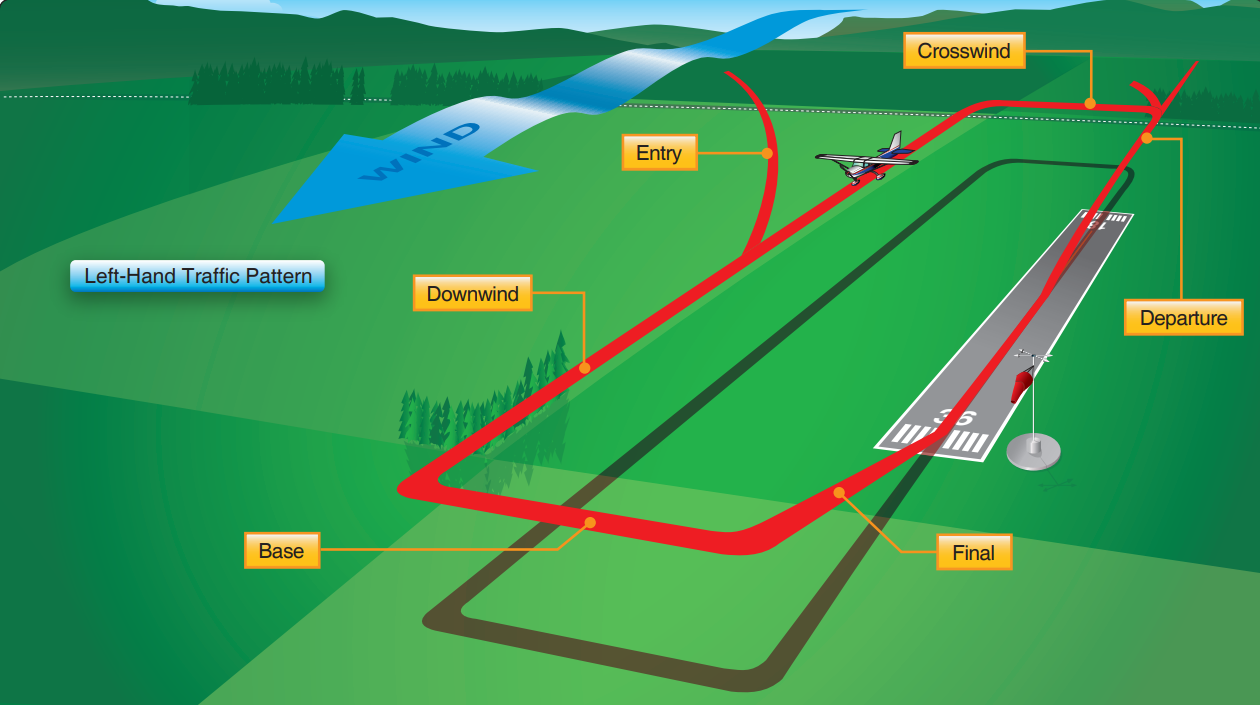
The Direction And Placement Of The Pattern, The Altitude At Which It Is To Be Flown, And The Procedures For Entering And Exiting The Pattern May Depend On Local Conditions.
It’s The Path You Will Fly When Leaving And Returning To The Airport, Specifically The Runway.
Related Post:
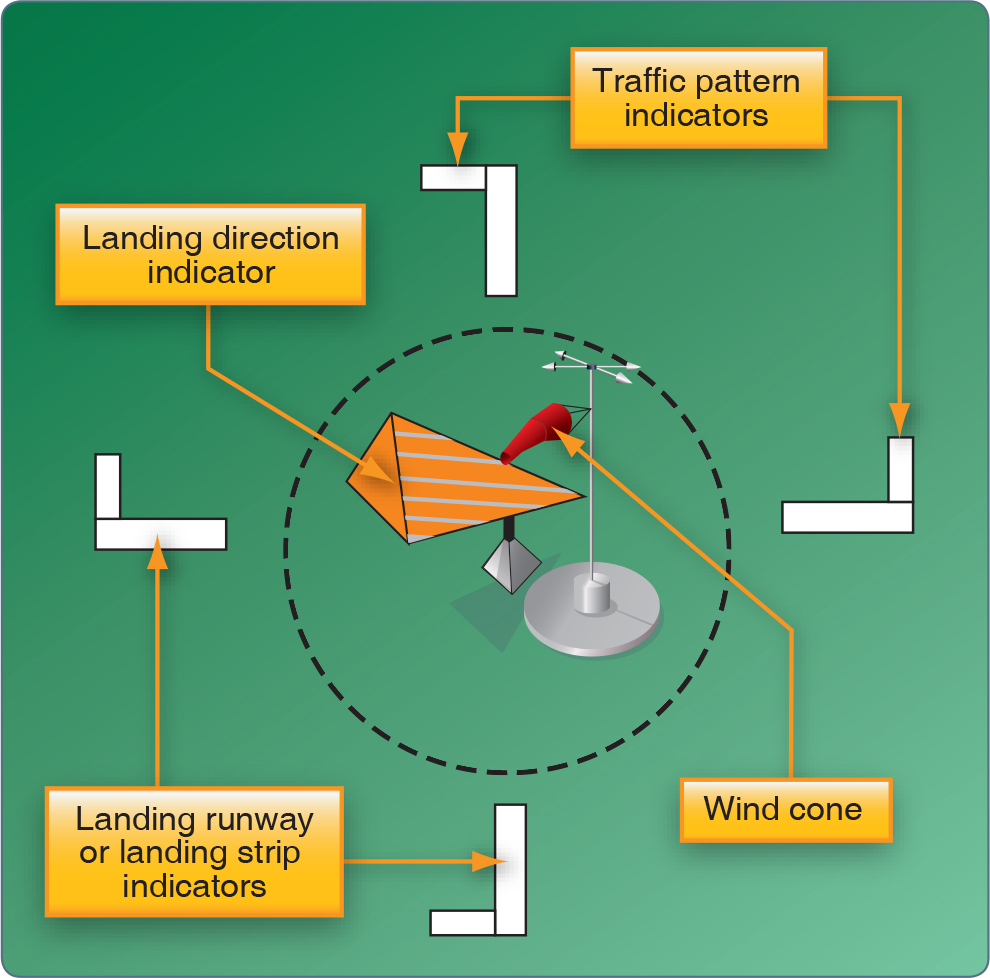


/Traffic_patterns_depicted_in_FAA-H-8083-25-56a058ce3df78cafdaa1229b.jpg)