Furrow Pattern Acral Nevus
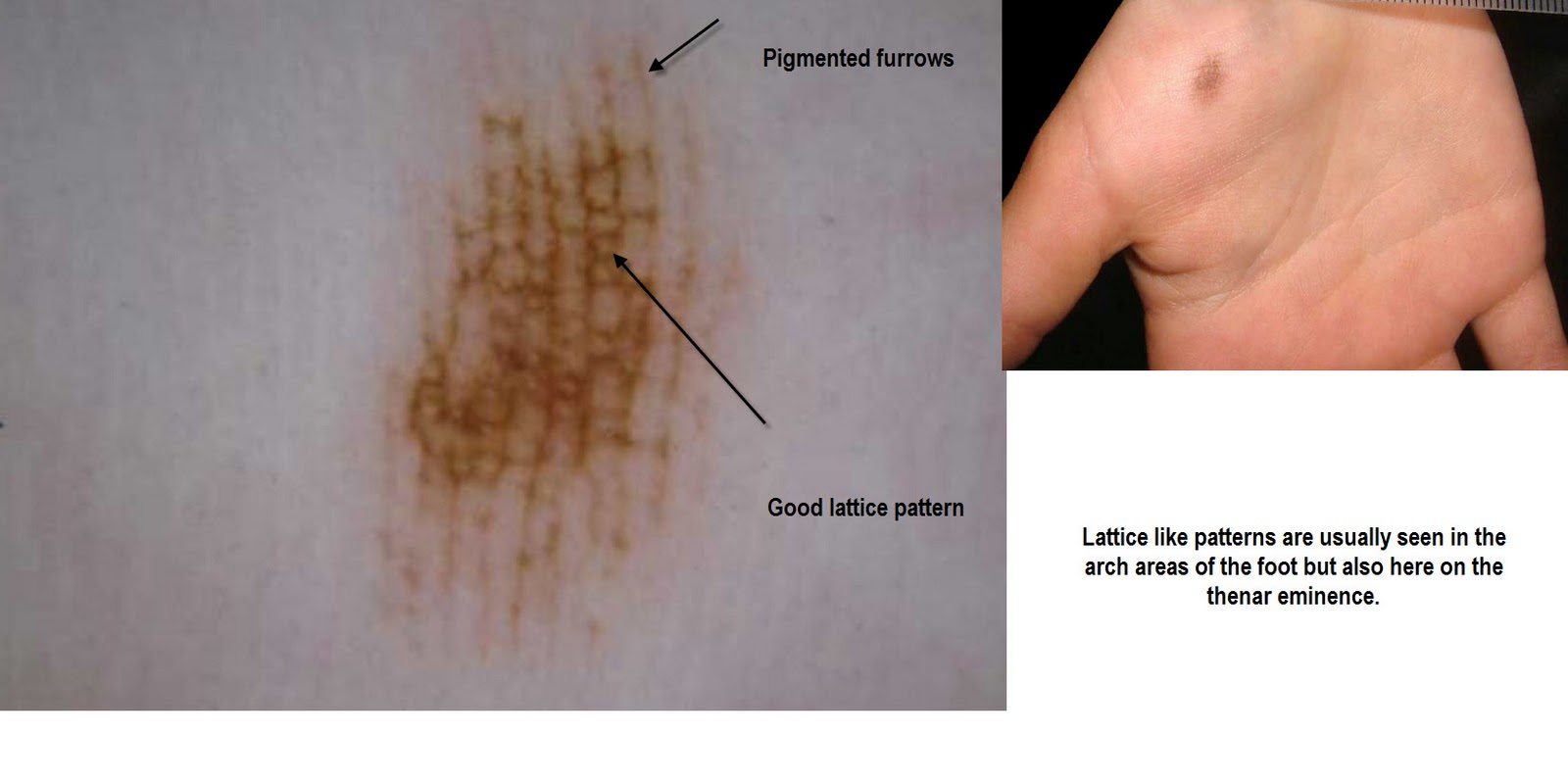
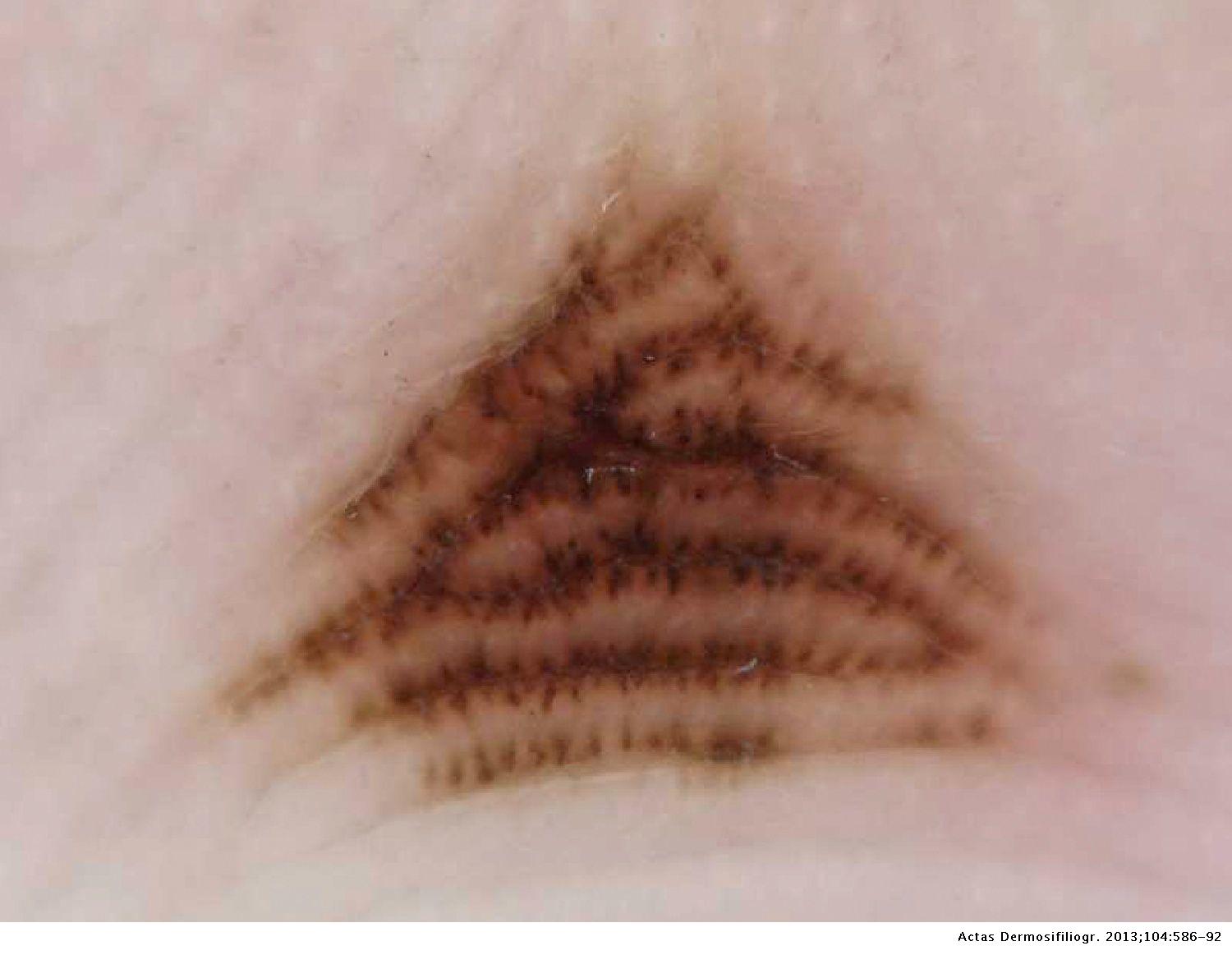
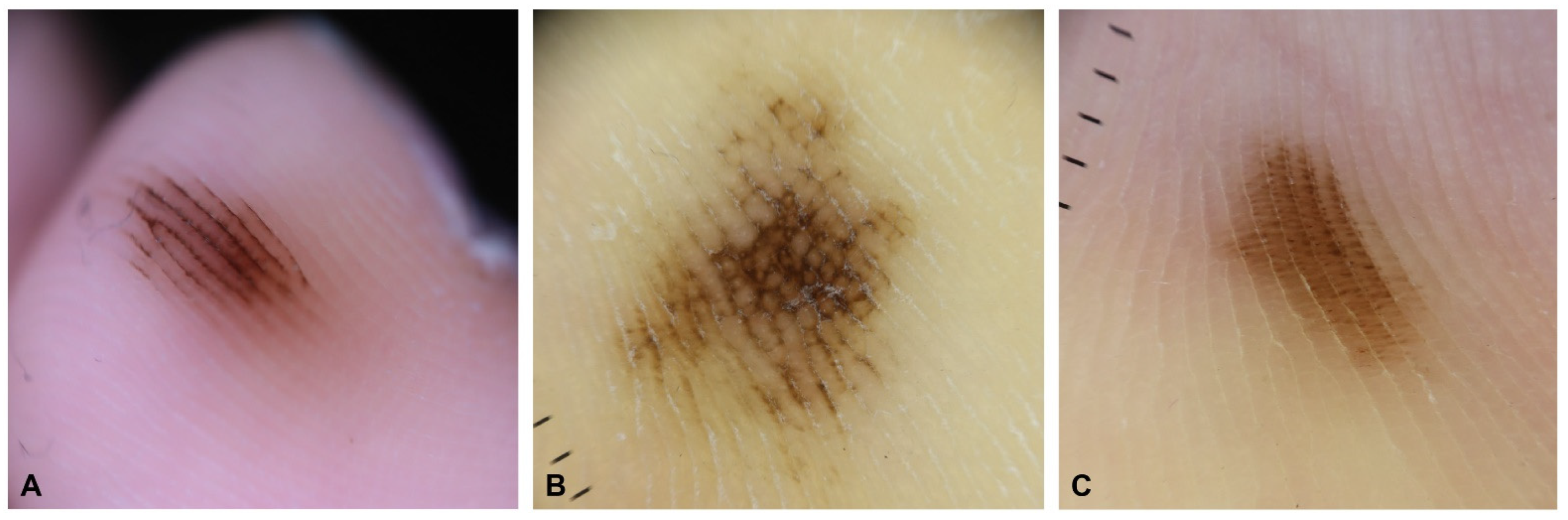
Furrow Pattern Acral Nevus - 100%, p = 0.035), irregular diffuse pigmentation (27.3% vs. Pigmentation on the ridges of the surface skin markings is detected in early acral melanoma, whereas pigmentation along the furrows of the skin markings is seen in acral nevus. Web among acral nevi, the parallel furrow (42.1%) was the most common pattern, followed by the latticelike (14.9%), nontypical (13.7%), fibrillar (10.8%), homogeneous (9.3%), globular (5.4%), and reticular (2.1%) patterns. [1] the example images have been approved by a panel of experts as representative of each given feature. Pigmentation along the furrows of the skin markings is characteristic of acral naevus. Web the parallel furrow pattern is the most common (a). Web fig 1 acral nevus. Web dermoscopic pigmentation pattern is helpful in distinguishing an acral lentiginous melanoma and a benign acral nevus. Transition pattern observed on the lateral aspect of the heel. These dermoscopic patterns are termed the parallel ridge pattern and the parallel furrow pattern, respectively. More than 75% of benign acral lesions exhibit 1 of these major patterns. Web an automatic algorithm that can classify the “furrow” from “ridge” patterns of pigmentation on acral areas is proposed. Web acral melanocytic nevi have three major dermoscopic patterns: In a benign acral nevus, the pigmentation is along the furrows of the skin markings. Web acral lentiginous is the most common form of melanoma and occurs most often on the sole and beneath the toenail. Web if the lesion does not show the prp, we proceed to the second step in which we check whether it shows any of the typical dermoscopic patterns of benign acral nevus on the whole area of the lesion (typical parallel furrow pattern, typical latticelike pattern, or regular fibrillar pattern). Web fig 1 acral nevus. Pigmentation along the furrows of the skin markings is characteristic of acral naevus. 100%, p = 0.001) and grey colour (18.2%. Web this results in less ink adhering to the furrow, while allowing the ink to enter the openings of eccrine pores. Web numerous specific dermoscopic patterns have been defined for nevi and melanoma located on acral sites. However, as a rule, these nevi rarely affect the arch of the foot. 100%, p = 0.001) and grey colour (18.2%. Web this results in less ink adhering to the furrow, while allowing the ink to enter the openings of eccrine pores. 100%, p. Web the parallel furrow pattern is the most common (a). 100%, p = 0.001) and grey colour (18.2%. Even though the foot receives less solar exposure, it turns out pedal melanoma is more likely to kill patients than more proximal thigh melanoma. Web statistical analysis of dermoscopic features revealed that parallel ridge patterns (54.5% vs. Web dermoscopic pigmentation pattern is. Transition pattern observed on the lateral aspect of the heel. Web this results in less ink adhering to the furrow, while allowing the ink to enter the openings of eccrine pores. Pigmentation along the furrows of the skin markings is characteristic of acral naevus. Web numerous specific dermoscopic patterns have been defined for nevi and melanoma located on acral sites.. [1] the example images have been approved by a panel of experts as representative of each given feature. The parallel furrow pattern is regarded as the prototype of the three major dermoscopic. Web pigmentation pattern on dermoscopy is completely opposite between early acral melanoma and acral nevus; 100%, p = 0.035), irregular diffuse pigmentation (27.3% vs. In a benign acral. Web acral melanoma is an aggressive type of melanoma with unknown origins. Web in contrast, the main dermoscopic pattern of acral nevus is the parallel furrow pattern (pfp) showing linear pigmentation along the sulci of the skin markings. Web among acral nevi, the parallel furrow (42.1%) was the most common pattern, followed by the latticelike (14.9%), nontypical (13.7%), fibrillar (10.8%),. Web acral melanocytic nevi have three major dermoscopic patterns: Web if the lesion does not show the prp, we proceed to the second step in which we check whether it shows any of the typical dermoscopic patterns of benign acral nevus on the whole area of the lesion (typical parallel furrow pattern, typical latticelike pattern, or regular fibrillar pattern). Web. Web acral lentiginous is the most common form of melanoma and occurs most often on the sole and beneath the toenail. Web acral melanoma is an aggressive type of melanoma with unknown origins. Web in contrast, the main dermoscopic pattern of acral nevus is the parallel furrow pattern (pfp) showing linear pigmentation along the sulci of the skin markings. 100%,. Web in contrast, the main dermoscopic pattern of acral nevus is the parallel furrow pattern (pfp) showing linear pigmentation along the sulci of the skin markings. In a benign acral nevus, the pigmentation is along the furrows of the skin markings. In early acral melanoma, the pigmentation is present on the ridges of the skin surface markings. Web statistical analysis. Web this results in less ink adhering to the furrow, while allowing the ink to enter the openings of eccrine pores. Web statistical analysis of dermoscopic features revealed that parallel ridge patterns (54.5% vs. However, as a rule, these nevi rarely affect the arch of the foot. The furrow ink test is a quick and easy method to facilitate the. Web in contrast, the main dermoscopic pattern of acral nevus is the parallel furrow pattern (pfp) showing linear pigmentation along the sulci of the skin markings. Pigmentation on the ridges of the surface skin markings is detected in early acral melanoma, whereas pigmentation along the furrows of the skin markings is seen in acral nevus. Web acral lentiginous is the. Accurate discrimination is performed using the histogram analysis of dark/bright pattern width ratio. Even though the foot receives less solar exposure, it turns out pedal melanoma is more likely to kill patients than more proximal thigh melanoma. Web fig 1 acral nevus. Web the parallel furrow pattern is the most common (a). Web acral lentiginous is the most common form of melanoma and occurs most often on the sole and beneath the toenail. Web this results in less ink adhering to the furrow, while allowing the ink to enter the openings of eccrine pores. Web numerous specific dermoscopic patterns have been defined for nevi and melanoma located on acral sites. Some variations of this pattern are represented in b through d. In a benign acral nevus, the pigmentation is along the furrows of the skin markings. Pigmentation along the furrows of the skin markings is characteristic of acral naevus. Web pigmentation on the ridges of the surface skin markings is characteristic of early acral melanoma. However, as a rule, these nevi rarely affect the arch of the foot. The parallel furrow pattern is regarded as the prototype of the three major dermoscopic. Web dermoscopic pigmentation pattern is helpful in distinguishing an acral lentiginous melanoma and a benign acral nevus. Pigmentation on the ridges of the surface skin markings is detected in early acral melanoma, whereas pigmentation along the furrows of the skin markings is seen in acral nevus. Web 5 peas in a pod pattern (parallel furrow + globules on ridges) (congenital nevi) below are dermoscopic features commonly associated with the diagnosis “benign patterns of acral nevi”.Dermoscopic Characteristics of Congenital Melanocytic Nevi Affecting
Dermoscopic Patterns of Acral Melanocytic Nevi Their Variations
Dermoscopic Patterns of 158 Acral Melanocytic Nevi in a Latin American
Dermoscopy Made Simple Acral nevus
Dermoscopy Made Simple Acral nevus
Regular fibrillar pattern of acral nevus (dermoscopy with the furrow
Variations in the Dermoscopic Features of Acquired Acral Melanocytic
Dermoscopic Patterns of 158 Acral Melanocytic Nevi in a Latin American
Dermatopathology Free FullText Acral Melanocytic Neoplasms A
Dermoscopy Made Simple Acral nevus
Web Statistical Analysis Of Dermoscopic Features Revealed That Parallel Ridge Patterns (54.5% Vs.
In Early Acral Melanoma, The Pigmentation Is Present On The Ridges Of The Skin Surface Markings.
Web Melanocytic Nevi Showing The Parallel Furrow Or Fibrillar Pattern Are Predominantly Located On The Foot, In Which Case A Regular Parallel Distribution Of Skin Markings Is Observed.
Web An Automatic Algorithm That Can Classify The “Furrow” From “Ridge” Patterns Of Pigmentation On Acral Areas Is Proposed.
Related Post: