Strain Pattern Ecg
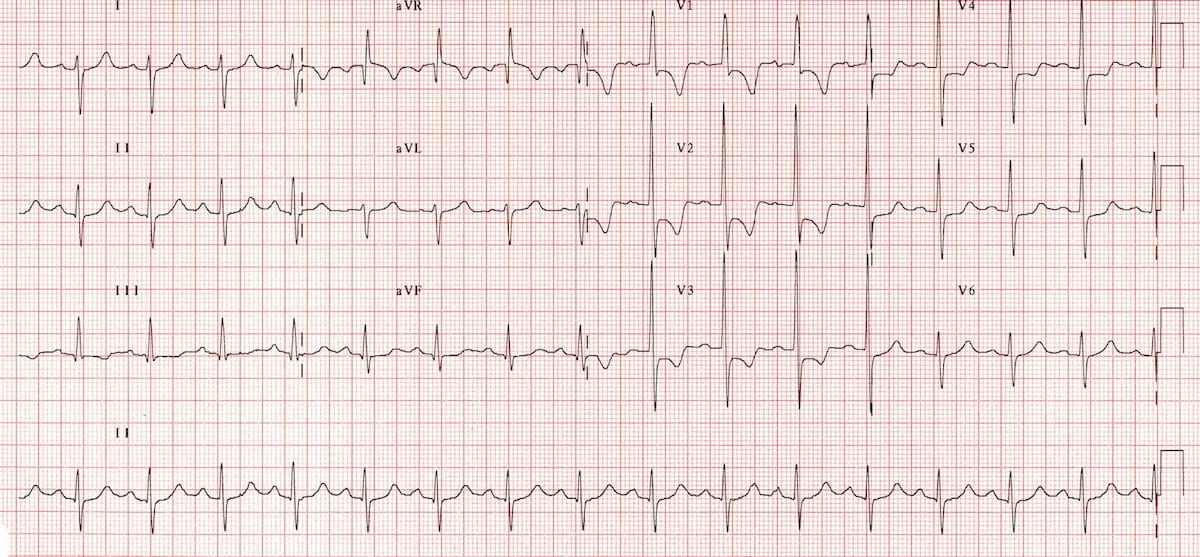
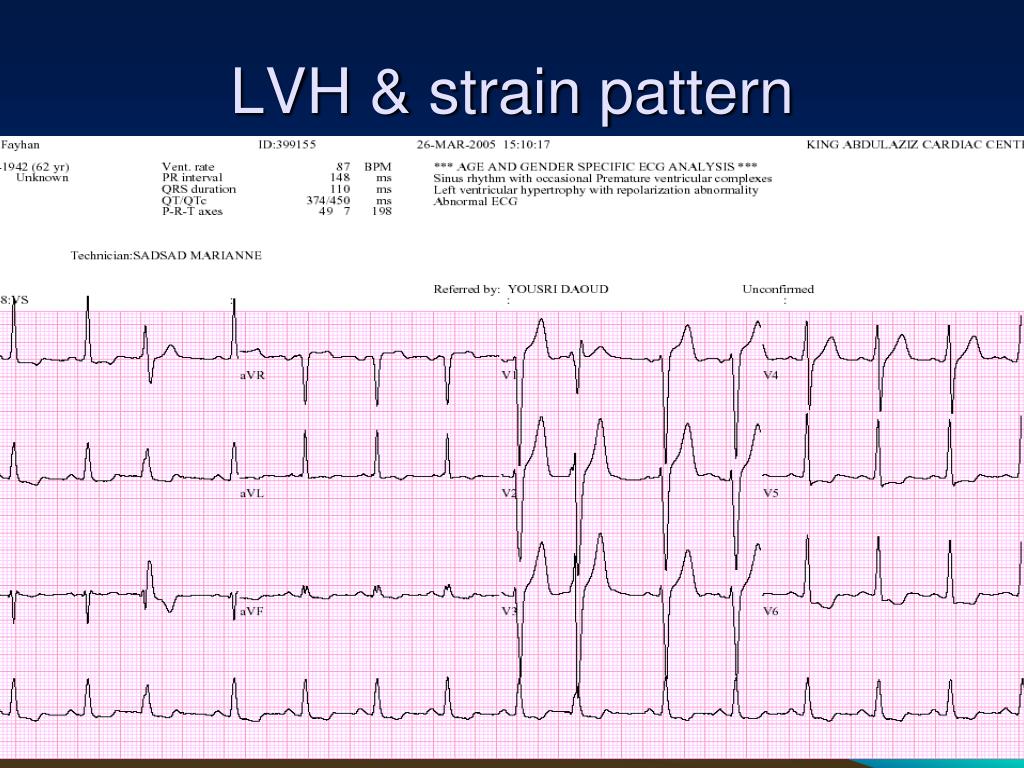
Strain Pattern Ecg - The limitations of the ecg relate to its moderate sensitivity or specificity depending upon which of the many proposed sets of diagnostic criteria are applied [ 1,2 ]. Web the most commonly observed pattern is asymmetrical thickening of the anterior interventricular septum (= asymmetrical septal hypertrophy ). Web the most common ecg dilemmas one encounters is to differentiate between the st segment depression and t wave inversion due to lvh from that of primary ischemia. Web baseline characteristics of patients with and without ecg strain. Huge precordial r and s waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (sv2 + rv6 >> 35 mm). The same data quoted specificity ranging from 89.8% to 100%. This ecg is from a man with left ventricular hypertrophy. Recently, ecg strain pattern has been shown to be associated with inappropriate left ventricular hypertrophy. Web this multiethnic study of adults without past cardiovascular disease showed that ecg strain is associated with a higher risk for all‐cause death, incident heart failure, myocardial infarction, and incident cardiovascular disease independent of ecg left ventricular (lv) hypertrophy measured by qrs. We investigated the mechanisms and outcomes associated with ecg strain. The sensitivity of lvh strain pattern on ecg as a measure of lvh has ranged from 3.8% to 50% in various reports [1]. Web left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh): Web baseline characteristics of patients with and without ecg strain. This pattern has been classically associated with systolic anterior motion (sam) of the mitral valve and dynamic left ventricular outflow tract (lvot) obstruction. Very often , the entity is misdiagnosed. Huge precordial r and s waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (sv2 + rv6 >> 35 mm). Web the strain pattern in the 12‐lead ecg, defined as st‐segment depression and t‐wave inversion, represents ventricular repolarization abnormalities.1 the mechanism underlying ecg strain is unclear, although it has been proposed as subendocardial ischemia.2, 3 ecg strain is associated with concentric left ventricular (lv) hypertrophy. Web lvh with strain pattern can sometimes be seen in long standing severe aortic regurgitation, usually with associated left ventricular hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction. Web the most common ecg dilemmas one encounters is to differentiate between the st segment depression and t wave inversion due to lvh from that of primary ischemia. Web ecg changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) and right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh). Web left ventricular hypertrophy with strain. Web the most commonly observed pattern is asymmetrical thickening of the anterior interventricular septum (= asymmetrical septal hypertrophy ). 2,6 ecg strain has been. Web baseline characteristics of patients with and without ecg strain. Recently, ecg strain pattern has been shown to be associated with inappropriate left ventricular hypertrophy. Web the most commonly observed pattern is asymmetrical thickening of the anterior interventricular septum (= asymmetrical septal hypertrophy ). This pattern has been classically associated with systolic anterior motion (sam) of the mitral valve and dynamic left ventricular outflow tract (lvot) obstruction. The sensitivity of lvh strain pattern on ecg as a measure of lvh has ranged from 3.8% to. This ecg is from a man with left ventricular hypertrophy. The sensitivity of lvh strain pattern on ecg as a measure of lvh has ranged from 3.8% to 50% in various reports [1]. Web the electrocardiogram (ecg) is a useful but imperfect tool for detecting lvh. Web ecg left ventricular hypertrophy with strain is associated with an adverse prognosis in. Web ecg strain pattern was associated with poorer lv systolic function and abnormal lv geometry, particularly eccentric lvh. Web ecg changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh) and right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh). Web the strain pattern in the 12‐lead ecg, defined as st‐segment depression and t‐wave inversion, represents ventricular repolarization abnormalities.1 the mechanism underlying ecg strain is unclear, although it has. The limitations of the ecg relate to its moderate sensitivity or specificity depending upon which of the many proposed sets of diagnostic criteria are applied [ 1,2 ]. Web lvh with strain pattern can sometimes be seen in long standing severe aortic regurgitation, usually with associated left ventricular hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction. It also is easier to diagnose in supraventricular. Web right ventricular strain is a repolarisation abnormality due to right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh) or dilatation. Web the strain pattern in the 12‐lead ecg, defined as st‐segment depression and t‐wave inversion, represents ventricular repolarization abnormalities.1 the mechanism underlying ecg strain is unclear, although it has been proposed as subendocardial ischemia.2, 3 ecg strain is associated with concentric left ventricular (lv). Web left ventricular hypertrophy with strain pattern (example 3) | learn the heart. Web the most common ecg dilemmas one encounters is to differentiate between the st segment depression and t wave inversion due to lvh from that of primary ischemia. It also is easier to diagnose in supraventricular rhythms, because ventricular rhythms usually have large qrs complexes due to. Web left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh): Typical lv strain pattern was presented on ecgs of 101 patients (23%). Web left ventricular hypertrophy with strain pattern ecg (example 1) | learn the heart. Web the most commonly observed pattern is asymmetrical thickening of the anterior interventricular septum (= asymmetrical septal hypertrophy ). Web left ventricular hypertrophy with strain pattern (example 3) |. The sensitivity of lvh strain pattern on ecg as a measure of lvh has ranged from 3.8% to 50% in various reports [1]. Web left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh): Web left ventricular hypertrophy with strain pattern (example 3) | learn the heart. It also is easier to diagnose in supraventricular rhythms, because ventricular rhythms usually have large qrs complexes due to. Huge precordial r and s waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (sv2 + rv6 >> 35 mm). St depression and t wave inversion in leads corresponding to the right ventricle: Web the strain pattern in the 12‐lead ecg, defined as st‐segment depression and t‐wave inversion, represents ventricular repolarization abnormalities.1 the mechanism underlying ecg strain is unclear, although it has. The limitations of the ecg relate to its moderate sensitivity or specificity depending upon which of the many proposed sets of diagnostic criteria are applied [ 1,2 ]. Web left ventricular hypertrophy with strain pattern ecg (example 1) | learn the heart. Web the most common ecg dilemmas one encounters is to differentiate between the st segment depression and t wave inversion due to lvh from that of primary ischemia. The same data quoted specificity ranging from 89.8% to 100%. Web left ventricular hypertrophy (lvh): Web the most commonly observed pattern is asymmetrical thickening of the anterior interventricular septum (= asymmetrical septal hypertrophy ). 2,6 ecg strain has been. St depression and t wave inversion in leads corresponding to the right ventricle: Web ecg left ventricular hypertrophy with strain is associated with an adverse prognosis in aortic stenosis. This ecg is from a man with left ventricular hypertrophy. Web the electrocardiogram (ecg) is a useful but imperfect tool for detecting lvh. Web there will be discordant st segments and t waves, which is called the strain pattern. We investigated the mechanisms and outcomes associated with ecg strain. Web right ventricular strain is a repolarisation abnormality due to right ventricular hypertrophy (rvh) or dilatation. Web this multiethnic study of adults without past cardiovascular disease showed that ecg strain is associated with a higher risk for all‐cause death, incident heart failure, myocardial infarction, and incident cardiovascular disease independent of ecg left ventricular (lv) hypertrophy measured by qrs. Web baseline characteristics of patients with and without ecg strain.ECG Class Keeping ECGs Simple ECGclass Summer 3 Aortic Stenosis
Right Ventricular Strain • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
Strain, strain rate and speckle tracking Myocardial deformation ECG
Prognostic Value of Changes in the Electrocardiographic Strain Pattern
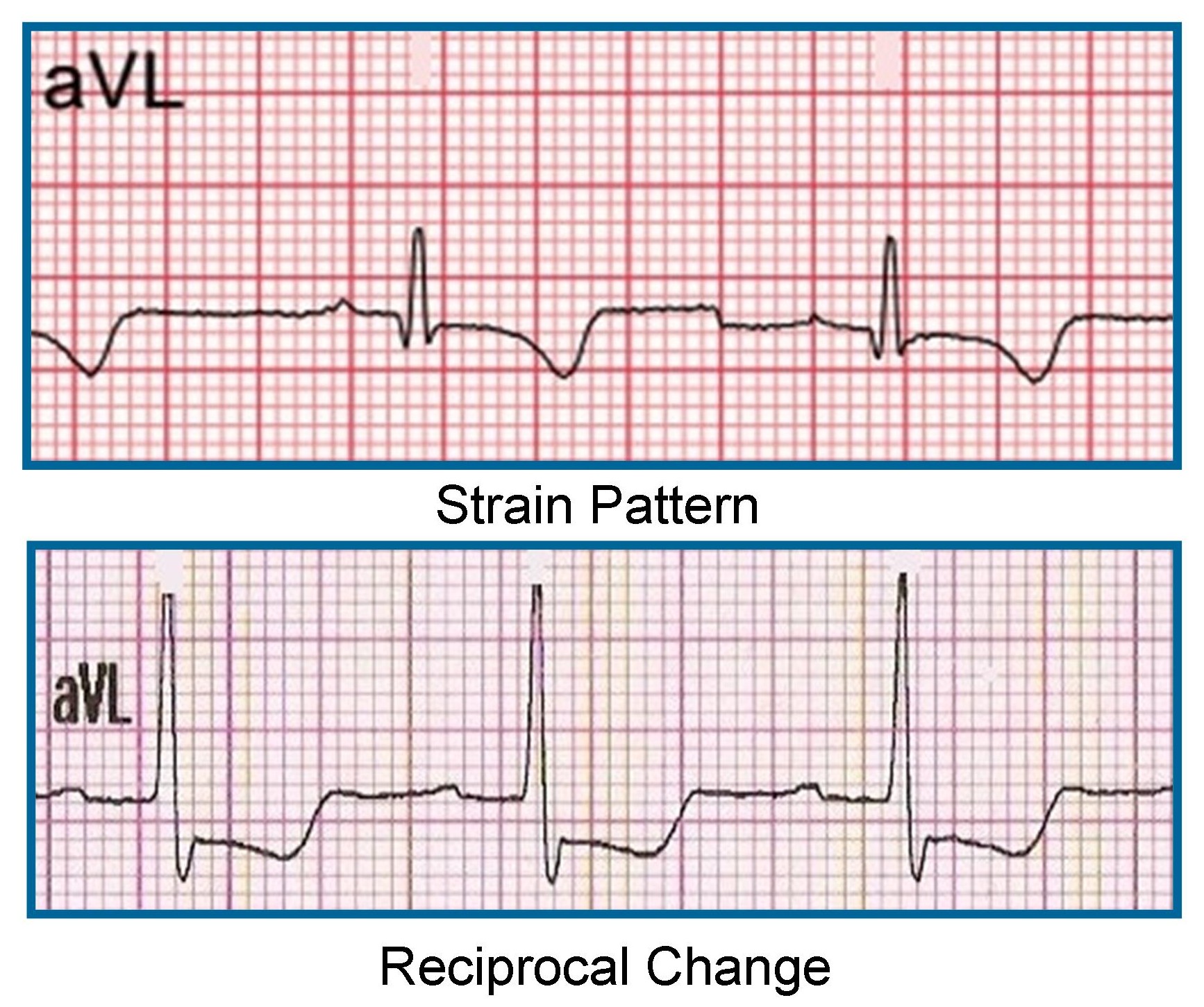
Importance of Lead aVL in STEMI Recognition ECG Medical Training
PPT ECG PRACTICAL APPROACH PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Right Heart Strain ECG Stampede
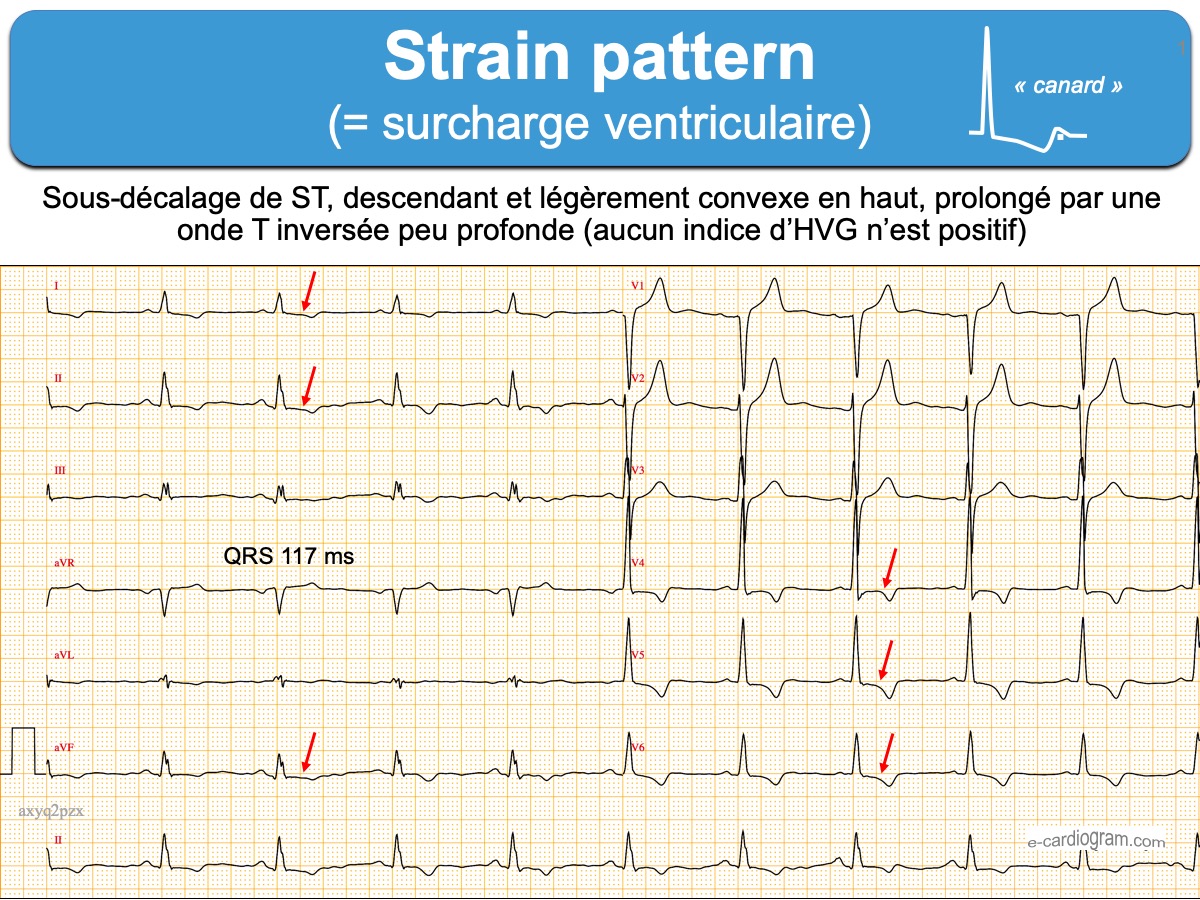
Strain pattern ecardiogram
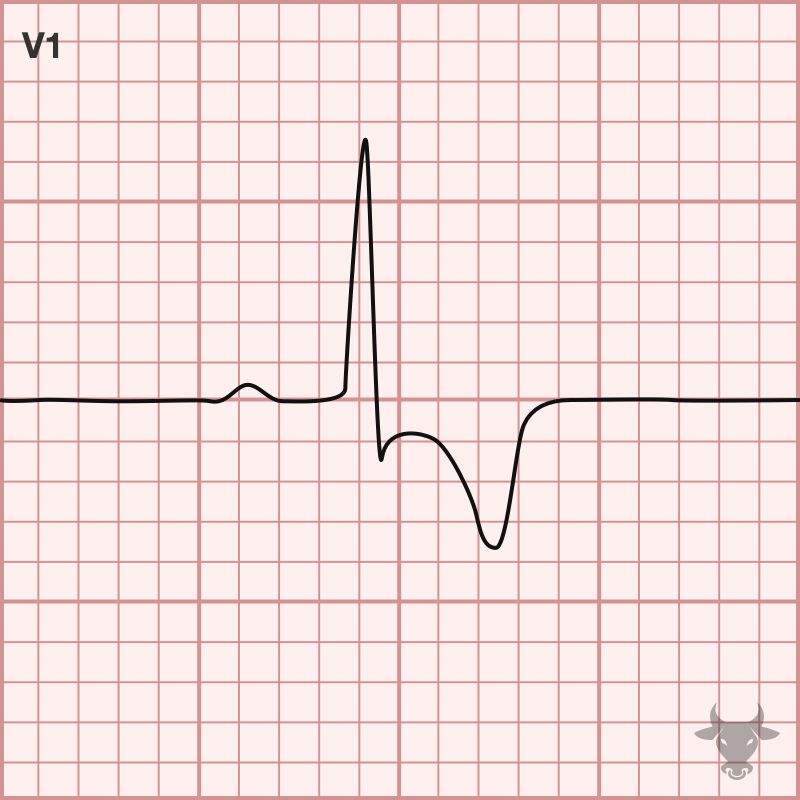
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) ECG criteria & clinical
ECG Interpretation ECG Interpretation Review 51 (Chamber Enlargement
Web The Strain Pattern In The 12‐Lead Ecg, Defined As St‐Segment Depression And T‐Wave Inversion, Represents Ventricular Repolarization Abnormalities.1 The Mechanism Underlying Ecg Strain Is Unclear, Although It Has Been Proposed As Subendocardial Ischemia.2, 3 Ecg Strain Is Associated With Concentric Left Ventricular (Lv) Hypertrophy.
Web Left Ventricular Hypertrophy With Strain Pattern (Example 3) | Learn The Heart.
Web Lvh With Strain Pattern Can Sometimes Be Seen In Long Standing Severe Aortic Regurgitation, Usually With Associated Left Ventricular Hypertrophy And Systolic Dysfunction.
Huge Precordial R And S Waves That Overlap With The Adjacent Leads (Sv2 + Rv6 >> 35 Mm).
Related Post:



.jpg)